1897

He became a Fellow of Trinity College in 1880, when he was Second Wrangler and Second Smith’s Prizeman, and he remained a member of the College for the rest of his life, becoming Lecturer in 1883 and Master in 1918. He was Cavendish Professor of Experimental Physics at Cambridge, where he succeeded Lord Rayleigh, from 1884 to 1918 and Honorary Professor of Physics, Cambridge and Royal Institution, London.
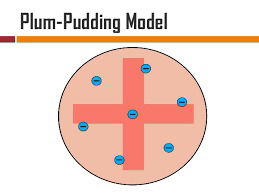
In 1897, Joseph John Thomson (1856–1940) had announced the discovery of a corpuscle. Others soon called it ► electron, despite Thomson's stubborn preference for his original term, borrowed from Robert Boyle (1627–91) to denote any particlelike structure. Very soon afterwards, Thomson began to think about how to explain the periodicity of properties of the chemical elements in terms of these negatively charged corpuscles as atomic constituents. Chemical properties would thus have to depend on the number and constellations of these corpuscles inside the atom. They would have to have stable positions in it, bound by electrostatic and possibly kinetic forces. Because under normal conditions chemical atoms are electrically neutral, the total electric charge of all these negatively charged electrons had to be compensated for by an equal amount of positive charge. For Thomson it was natural to assume that this positive charge was continuously distributed throughout the atom, whose radius was estimated at the time to be around 10−12 m. The very small negatively charged electrons (contemporary estimates indicated an order of magnitude of 10−15 m) were distributed in the atom like raisins inside a cake or like plums in a pudding, whence the popular nickname for Thomson's atomic model as the “plum pudding model”.
